Wireless Transport Layer Security (WTLS)
Wireless Transport Layer Service is an optional protocol which provides bearer-level security, in a way similar to TLS for end-to-end security. If the wireless bearer already provides over-the-air security (to make eavesdropping more difficult by encrypting the data sent over the air), then WTLS is not required. This is the case for GSM CSD and GSM GPRS for example.
History
XXX - add a brief description of WTLS history
Protocol dependencies
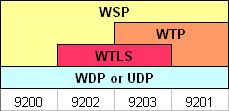
Depending on the protocol stack, 4 different standard WDP (UDP) ports have been defined. When WTLS is used, then the ports are 9202 (CL-WSP) and 9203 (CO-WSP). WSP can run on other ports too.
-
WDP: On non-IP bearers, WTLS uses WDP as its transport protocol.
-
UDP: On IP-enabled bearers (such as GPRS and GSM CSD) WTLS uses UDP as its transport protocol.
Example traffic
XXX - Add example traffic here (as plain text or Wireshark screenshot).
Wireshark
The WTLS dissector is fully functional. Decryption however is not provided yet.
Preference Settings
There are no preferences for WTLS in Wireshark.
Example capture file
XXX - Add a simple example capture file to the SampleCaptures page and link from here. Keep it short, it's also a good idea to gzip it to make it even smaller, as Wireshark can open gzipped files automatically.
Display Filter
A complete list of WTLS display filter fields can be found in the display filter reference
Show only the WTLS based traffic:
wtls Capture Filter
You cannot directly filter WTLS traffic while capturing. However, if you know the transport protocol (bearer) used (see above), you can filter on that one.
External links
- See the WAP Forum and the Open Mobile Alliance.
Discussion
Imported from https://wiki.wireshark.org/Wireless_Transport_Layer_Security on 2020-08-11 23:27:35 UTC