OpenVPN Protocol (OpenVPN)
With OpenVPN, you can tunnel any IP subnetwork or virtual ethernet adapter over a single UDP or TCP port. It uses all of the encryption, authentication, and certification features of the OpenSSL library to protect your private network traffic as it transits the internet.
OpenVPN has two authentication modes:
- Static Key - Use a pre-shared static key
- TLS - Use SSL/TLS + certificates for authentication and key exchange
For TLS authentication OpenVPN uses a custom security protocol which is described here on this WIKI page. This protocol provides the SSL/TLS connection with a reliable transport layer (as it is designed to operate over). It's second job is to multiplex the SSL/TLS session used for authentication and key exchange with the actual encrypted tunnel data stream.
SSL/TLS -> Reliability Layer -> \
--tls-auth HMAC \
\
> Multiplexer ----> UDP
/ Transport
IP Encrypt and HMAC /
Tunnel -> using OpenSSL EVP --> /
Packets interface.History
I couldn't find any historical information about this protocol.
Protocol dependencies
-
UDP: Typically, OpenVPN uses UDP as its transport protocol. The well known UDP port for OpenVPN traffic is 1194.
-
TCP: Additionally, OpenVPN can be configured to use TCP as its transport protocol. The well known TCP port for OpenVPN traffic is 1194.
Example traffic
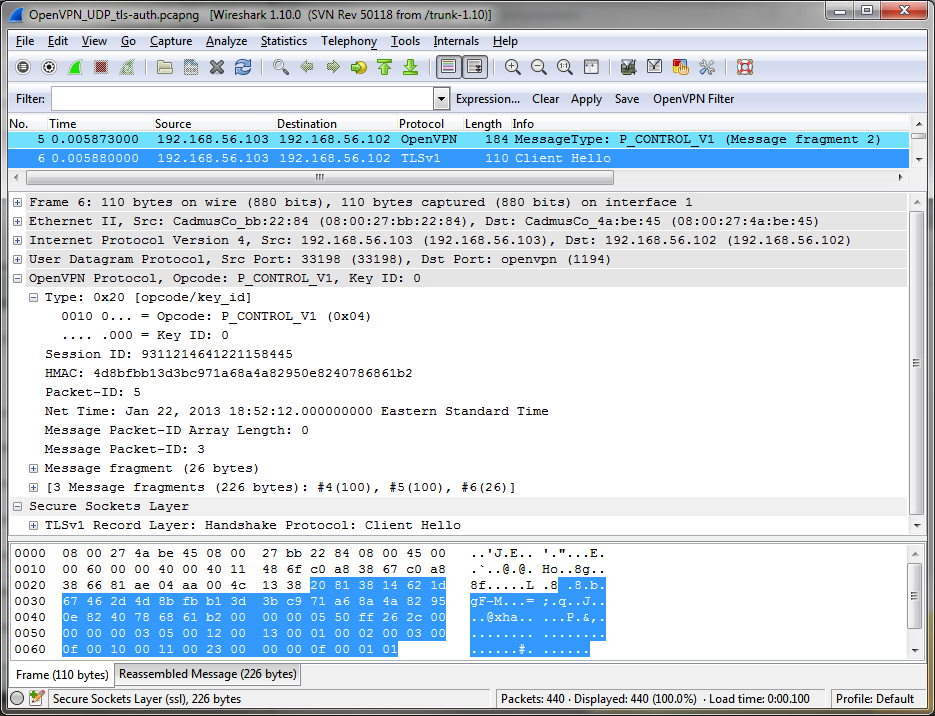
Wireshark
The OpenVPN dissector is fully functional and included with Wireshark as of version 1.10.0.
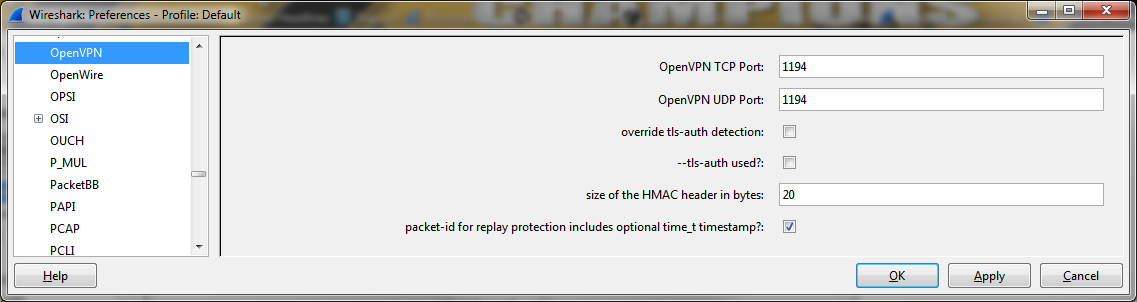
Preference Settings
-
OpenVPN TCP Port: The dissector automatically tries to dissect TCP packets as OpenVPN traffic on this port.
-
OpenVPN UDP Port: The dissector automatically tries to dissect UDP datagrams as OpenVPN traffic on this port.
-
override tls-auth detection: If tls-auth detection fails, you can choose to override detection and set the tls-auth options manually.
-
--tls-auth used?: If the parameter --tls-auth is used, the following preferences must also be defined.
-
size of the HMAC header in bytes: The default HMAC algorithm is SHA-1 which generates a 160 bit HMAC, therefore 20 bytes should be ok.
-
packet-id for replay protection includes optional time_t timestamp?: If the parameter --tls-auth is used, an additional packet-id for replay protection is inserted after the HMAC signature. This field can either be 4 bytes or 8 bytes including an optional time_t timestamp long. The default value is True.
-
-
Example capture file
Display Filter
A complete list of OpenVPN display filter fields can be found in the display filter reference
Show only the OpenVPN based traffic:
openvpn Capture Filter
You cannot directly filter OpenVPN protocols while capturing. However, if you know the UDP or TCP port used (see above), you can filter on that one.
Capture only the openvpn traffic over the default port (1194):
udp port 1194 or
tcp port 1194 External links
-
http://openvpn.net/ OpenVPN - Official Website.
-
http://openvpn.net/index.php/open-source/documentation/security-overview.html OpenVPN - Security Overview - The OpenVPN protocol explained.
-
http://www.openssl.org/ OpenSSL - Official Website.
Discussion
Imported from https://wiki.wireshark.org/OpenVPN on 2020-08-11 23:17:42 UTC