MATE: Manual
This manual will give you a detailed description of how MATE works.
Table of contents
- MATE: Manual
Introduction
MATE creates a filterable tree based on information contained in frames that share some relationship with information obtained from other frames. The way this relationships are made is described in a configuration file. The configuration file tells MATE what makes a PDU and how to relate it to other PDUs.
MATE analyzes each frame to extract relevant information from the "protocol" tree of that frame. The extracted information is contained in MATE PDUs; these contain a list of relevant attributes taken from the tree. From now on, I will use the term "PDU" to refer to the objects created by MATE containing the relevant information extracted from the frame; I'll use "frame" to refer to the "raw" information extracted by the various dissectors that pre-analyzed the frame.
For every PDU, MATE checks if it belongs to an existing "Group of PDUs" (Gop). If it does, it assigns the PDU to that Gop and moves any new relevant atributes to the Gop's attribute list. How and when do PDUs belong to Gops is described in the configuration file as well.
Every time a Gop is assigned a new PDU, MATE will check if it matches the conditions to make it belong to a "Group of Groups" (Gog). Naturally the conditions that make a Gop belong to a Gog are taken from the configuration file as well.
Once MATE is done analyzing the frame it will be able to create a "protocol" tree for each frame based on the PDUs, the Gops they belong to and naturally any Gogs the former belongs to.
How to tell MATE what to extract, how to group it and then how to relate those groups is made using AVPs and AVPLs.
Information in MATE is contained in Attribute/Value Pairs (AVPs). AVPs are made of two strings: the name and the value. AVPs are used in the configuration and there they have an operator as well. There are various ways AVPs can be matched against each other using those operators.
AVPs are grouped into AVP Lists (AVPLs). PDUs, Gops and Gogs have an AVPL each. Their AVPLs will be matched in various ways against others coming from the configuration file.
MATE will be instructed how to extract AVPs from frames in order to create a PDU with an AVPL. It will be instructed as well, how to match that AVPL against the AVPLs of other similar PDUs in order to relate them. In MATE the relationship between PDUs is a Gop, it has an AVPL as well. MATE will be configured with other AVPLs to operate against the Gop's AVPL to relate Gops together into Gogs.
A good understanding on how AVPs and AVPLs work is fundamental to understand how MATE works.
Attribute Value Pairs
Information used by MATE to relate different frames is contained in Attribute/Value Pairs (AVPs). AVPs are made of two strings - the name and the value. When AVPs are used in the configuration, an operator is defined as well. There are various ways AVPs can be matched against each other using those operators.
avp_name="avp's value"
another_name= "1234 is the value"The name is a string used to refer to a "kind" of an AVP. Two AVPs won't match unless their names are identical.
You should not use uppercase characters in names, or names that start with '.' or '_'. Capitalized names are reserved for configuration parameters (we'll call them keywords); nothing forbids you from using capitalized strings for other things as well but it probably would be confusing. I'll avoid using capitalized words for anything but the keywords in this document, the reference manual, the examples and the base library. Names that start with a '.' would be very confusing as well because in the old grammar, AVPL transformations use names starting with a '.' to indicate they belong to the replacement AVPL.
The value is a string that is either set in the configuration (for configuration AVPs) or by wireshark while extracting interesting fields from a frame's tree. The values extracted from fields use the same representation as they do in filter strings except that no quotes are used.
The name can contain only alphanumeric characters, "_", and ".". The name ends with an operator.
The value will be dealt with as a string even if it is a number. If there are any spaces in the value, the value must be between quotes "".
ip_addr=10.10.10.11,
tcp_port=1234,
binary_data=01:23:45:67:89:ab:cd:ef,
parameter12=0x23aa,
parameter_with_spaces="this value has spaces"The way two AVPs with the same name might match is described by the operator. Remember two AVPs won't match unless their names are identical. In MATE, match operations are always made between the AVPs extracted from frames (called data AVPs) and the configuration's AVPs.
Currently defined MATE's AVP match operators are:
-
Equal = will match if the string given completely matches the data AVP's value string
-
Not Equal ! will match only if the given value string is not equal to the data AVP's value string
-
One Of {} will match if one of the possible strings listed is equal to the data AVP's value string
-
Starts With ^ will match if the string given matches the first characters of the data AVP's value string
-
Ends With $ will match if the string given matches the last characters of the data AVP's value string
-
Contains ~ will match if the string given matches any substring of the data AVP's value string
-
Lower Than < will match if the data AVP's value string is semantically lower than the string given
-
Higher Than > will match if the data AVP's value string is semantically higher than the string given
-
Exists ? (the ? can be ommited) will match as far as a data AVP of the given name exists
AVP lists
An AVPL is a set of diverse AVPs that can be matched against other AVPLs. Every PDU, Gop and Gog has an AVPL that contains the information regarding it. The rules that MATE uses to group Pdus and Gops are AVPL operations.
There will never be two identical AVPs in a given AVPL. However, we can have more than one AVP with the same name in an AVPL as long as their values are different.
Some AVPL examples:
( addr=10.20.30.40, addr=192.168.0.1, tcp_port=21, tcp_port=32534, user_cmd=PORT, data_port=12344, data_addr=192.168.0.1 )
( addr=10.20.30.40, addr=192.168.0.1, channel_id=22:23, message_type=Setup, calling_number=1244556673 )
( addr=10.20.30.40, addr=192.168.0.1, ses_id=01:23:45:67:89:ab:cd:ef )
( user_id=pippo, calling_number=1244556673, assigned_ip=10.23.22.123 )In MATE there are two types of AVPLs:
- data AVPLs that contain information extracted from frames.
- operation AVPLs that come from the configuration and are used to tell MATE how to relate items based on their data AVPLs.
Data AVPLs can be operated against operation AVPLs in various ways:
-
Loose Match: Will match if at least one of the AVPs of each AVPL match. If it matches it will return an AVPL containing all AVPs from the operand AVPL that did match the operator's AVPs.
-
"Every" Match: Will match if none of the AVPs of the operator AVPL fails to match a present AVP in the operand AVPL, even if not all of the operator's AVPs have a match. If it matches it will return an AVPL containing all AVPs from the operand AVPL that did match one AVP in the operator AVPL.
-
Strict Match: Will match if and only if every one of the operator's AVPs have at least one match in the operand AVPL. If it matches it will return an AVPL containing the AVPs from the operand that matched.
-
There's also a Merge operation that is to be performed between AVPLs where all the AVPs that don't exist in the operand AVPL but exist in the operand will be added to the operand AVPL.
-
Other than that there are Transformations - a combination of a match AVPL and an AVPL to merge.
MATE Analysis
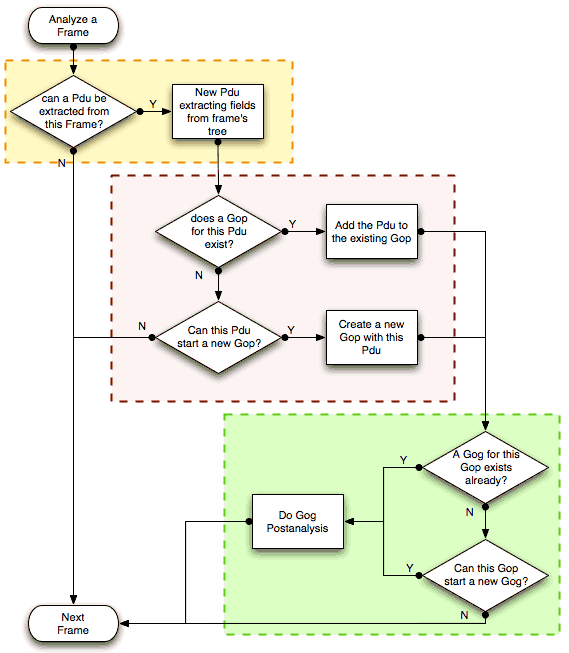
MATE's analysis of a frame is performed in three phases:
-
In the first phase, MATE attempts to extract a MATE Pdu from the frame's protocol tree. MATE will create a Pdu if MATE's config has a
Pdudeclaration whoseProtois contained in the frame. -
In the second phase, if a Pdu has been extracted from the frame, MATE will try to group it to other Pdus into a Gop (Group of Pdus) by matching the key criteria given by a
Gopdeclaration. If there is no Gop yet with the key criteria for the Pdu, MATE will try to create a new Gop for it if it matches theStartcriterium given in theGopdeclaration. -
In the third phase, if there's a Gop for the Pdu, MATE will try to group this Gop with other Gops into a Gog (Group of Groups) using the criteria given by the
Membercriteria of aGogdeclaration.
The extraction and matching logic comes from MATE's configuration; MATE's configuration file is declared by the mate.config preference. By default it is an empty string which means: do not configure MATE.
The config file tells MATE what to look for in frames; How to make PDUs out of it; How will PDUs be related to other similar PDUs into Gops; And how Gops relate into Gogs.
The MATE configuration file is a list of declarations. There are 4 types of declarations: Transform, Pdu, Gop and Gog.
Mate's PDUs
MATE will look in the tree of every frame to see if there is useful data to extract, and if there is, it will create one or more PDU objects containing the useful information.
The first part of MATE's analysis is the "PDU extraction"; there are various "Actions" that are used to instruct MATE what has to be extracted from the current frame's tree into MATE's PDUs.
PDU data extraction
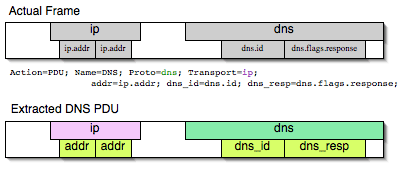
MATE will make a Pdu for each different proto field of Proto type present in the frame. MATE will fetch from the field's tree those fields that are defined in the Mate/Reference declaration whose initial offset in the frame is within the boundaries of the current Proto and those of the given Transport and Payload statements.
Pdu dns_pdu Proto dns Transport ip {
Extract addr From ip.addr;
Extract dns_id From dns.id;
Extract dns_resp From dns.flags.response;
};MATE will make a Pdu for each different proto field of Proto type present in the frame. MATE will fetch from the field's tree those fields that are defined in the Pdu AVPL whose initial offset in the frame is within the boundaries of the current Proto and those of the various assigned Transports.
Once MATE has found a Proto field for which to create a Pdu from the frame it will move backwards in the frame looking for the respective Transport fields. After that it will create AVPs named as each of those given in the rest of the AVPL for every instance of the fields declared as its values.
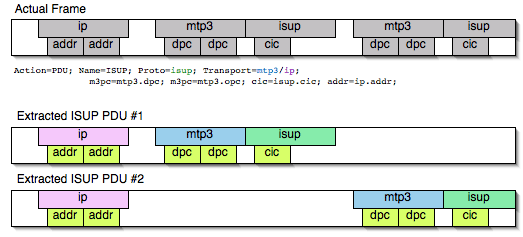
Sometimes we need information from more than one Transport protocol. In that case MATE will check the frame looking backwards to look for the various Transport protocols in the given stack. MATE will choose only the closest transport boundary per "protocol" in the frame.
This way we'll have all Pdus for every Proto that appears in a frame match its relative transports.
Pdu isup_pdu Proto isup Transport mtp3/ip {
Extract m3pc From mtp3.dpc;
Extract m3pc From mtp3.opc;
Extract cic From isup.cic;
Extract addr From ip.addr;
Extract isup_msg From isup.message_type;
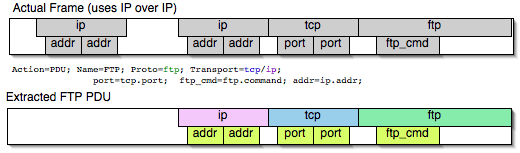
};This allows to assign the right Transport to the Pdu avoiding duplicate transport protocol entries (in case of tunneled ip over ip for example).
Pdu ftp_pdu Proto ftp Transport tcp/ip {
Extract addr From ip.addr;
Extract port From tcp.port;
Extract ftp_cmd From ftp.command;
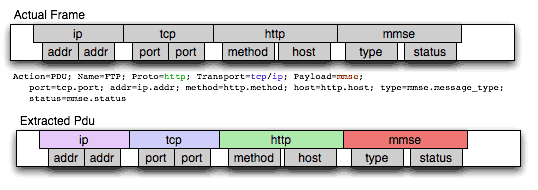
};Other than the mandatory Transport there is also an optional Payload statement, which works pretty much as Transport but refers to elements after the Proto's range. It is useful in those cases where the payload protocol might not appear in a Pdu but nevertheless the Pdu belongs to the same category.
Pdu mmse_over_http_pdu Proto http Transport tcp/ip {
Payload mmse;
Extract addr From ip.addr;
Extract port From tcp.port;
Extract method From http.request.method;
Extract content From http.content_type;
Extract http_rq From http.request;
Extract resp From http.response.code;
Extract host From http.host;
Extract trx From mmse.transaction_id;
Extract msg_type From mmse.message_type;
Extract notify_status From mmse.status;
Extract send_status From mmse.response_status;
};Conditions on which to create PDUs
There might be cases in which we won't want MATE to create a PDU unless some of its extracted attributes meet or do not meet some criteria. For that we use the Criteria statements of the Pdu declarations.
Pdu isup_pdu Proto isup Transport mtp3/ip {
...
// MATE will create isup_pdu PDUs only when there is not a point code '1234'
Criteria Reject Strict (m3pc=1234);
};
Pdu ftp_pdu Proto ftp Transport tcp/ip {
...
// MATE will create ftp_pdu PDUs only when they go to port 21 of our ftp_server
Criteria Accept Strict (addr=10.10.10.10, port=21);
};The Criteria statement is given an action (Accept or Reject), a match mode (Strict, Loose or Every) and an AVPL against which to match the currently extracted one.
Transforming the attributes of a PDU
Once the fields have been extracted into the Pdu's AVPL, MATE will apply any declared transformation to it. The way transforms are applied and how they work is described later on. However it's useful to know that once the AVPL for the Pdu is created, it may be transformed before being analyzed. That way we can massage the data to simplify the analysis.
MATE's PDU tree
Every successfully created Pdu will add a MATE tree to the frame dissection. If the Pdu is not related to any Gop, the tree for the Pdu will contain just the Pdu's info, if it is assigned to a Gop, the tree will also contain the Gop items, and the same applies for the Gog level.
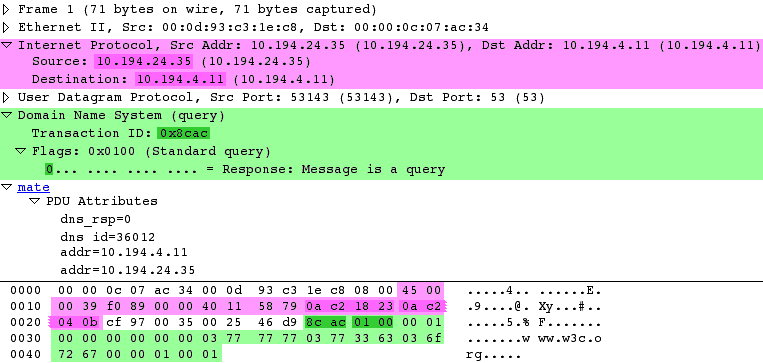
mate dns_pdu:1
dns_pdu: 1
dns_pdu time: 3.750000
dns_pdu Attributes
dns_resp: 0
dns_id: 36012
addr: 10.194.4.11
addr: 10.194.24.35The Pdu's tree contains some filterable fields
-
mate.dns_pdu will contain the number of the "dns_pdu" Pdu
-
mate.dns_pdu.RelativeTime will contain the time passed since the beginning of the capture in seconds
-
the tree will contain the various attributes of the Pdu as well, these will all be strings (to be used in filters as "10.0.0.1", not as 10.0.0.1)
- mate.dns_pdu.dns_resp
- mate.dns_pdu.dns_id
- mate.dns_pdu.addr
Grouping Pdus together (Gop)
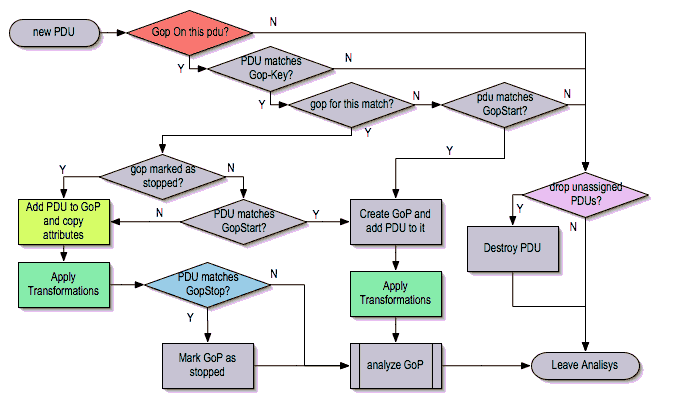
Once MATE has created the Pdus it passes to the Pdu analysis phase. During the PDU analysis phase MATE will try to group Pdus of the same type into Groups of Pdus (aka Gops) and copy some AVPs from the Pdu's AVPL to the Gop's AVPL.
What can belong to a Gop
Given a Pdu, the first thing MATE will do is to check if there is any Gop declaration in the configuration for the given Pdu type. If so, it will use its Match AVPL to match it against the Pdu's AVPL; if they don't match, the analysis phase is done. If there is a match, the AVPL is the Gop's candidate key which will be used to search the Gop's index for the Gop to which to assign the current PDU. If there is no such Gop and this Pdu does not match the Start criteria of a Gop declaration for the Pdu type, the Pdu will remain unassigned and only the analysis phase will be done.
Gop ftp_ses On ftp_pdu Match (addr, addr, port, port);
Gop dns_req On dns_pdu Match (addr, addr, dns_id);
Gop isup_leg On isup_pdu Match (m3pc, m3pc, cic);Start of a Gop
If there was a match, the candidate key will be used to search the Gop's index to see if there is already a Gop matching the Gop's key the same way. If there is such a match in the Gops collection, and the PDU doesn't match the Start AVPL for its kind, the PDU will be assigned to the matching Gop. If it is a Start match, MATE will check whether or not that Gop has been already stopped. If the Gop has been stopped, a new Gop will be created and will replace the old one in the Gop's index.
Gop ftp_ses On ftp_pdu Match (addr, addr, port, port) {
Start (ftp_cmd=USER);
};
Gop dns_req On dns_pdu Match (addr, addr, dns_id) {
Start (dns_resp=0);
};
Gop isup_leg On isup_pdu Match (m3pc, m3pc, cic) {
Start (isup_msg=1);
};If no Start is given for a Gop, a Pdu whose AVPL matches an existing Gog's key will act as the start of a Gop.
What goes into the Gop's AVPL
Once we know a Gop exists and the Pdu has been assigned to it, MATE will copy into the Gop's AVPL all the attributes matching the key plus any AVPs of the Pdu's AVPL matching the Extra AVPL.
Gop ftp_ses On ftp_pdu Match (addr, addr, port, port) {
Start (ftp_cmd=USER);
Extra (pasv_prt, pasv_addr);
};
Gop isup_leg On isup_pdu Match (m3pc, m3pc, cic) {
Start (isup_msg=1);
Extra (calling, called);
};End of a Gop
Once the Pdu has been assigned to the Gop, MATE will check whether or not the Pdu matches the Stop, if it happens, MATE will mark the Gop as stopped. Even after stopped, a Gop may get assigned new Pdus matching its key, unless such Pdu matches Start. If it does, MATE will instead create a new Gop starting with that Pdu.
Gop ftp_ses On ftp_pdu Match (addr, addr, port, port) {
Start (ftp_cmd=USER);
Stop (ftp_cmd=QUIT); // The response to the QUIT command will be assigned to the same Gop
Extra (pasv_prt, pasv_addr);
};
Gop dns_req On dns_pdu Match (addr, addr, dns_id) {
Start (dns_resp=0);
Stop (dns_resp=1);
};
Gop isup_leg On isup_pdu Match (m3pc, m3pc, cic) {
Start (isup_msg=1); // IAM
Stop (isup_msg=16); // RLC
Extra (calling, called);
};If no Stop criterium is stated for a given Gop, the Gop will be stopped as soon as it is created. However, as with any other Gop, Pdus matching the Gop's key will still be assigned to the Gop unless they match a Start condition, in which case a new Gop using the same key will be created.
Gop's tree
For every frame containing a Pdu that belongs to a Gop, MATE will create a tree for that Gop.
The example below represents the tree created by the dns_pdu and dns_req examples.
...
mate dns_pdu:6->dns_req:1
dns_pdu: 6
dns_pdu time: 2.103063
dns_pdu time since begining of Gop: 2.103063
dns_req: 1
dns_req Attributes
dns_id: 36012
addr: 10.194.4.11
addr: 10.194.24.35
dns_req Times
dns_req start time: 0.000000
dns_req hold time: 2.103063
dns_req duration: 2.103063
dns_req number of PDUs: 2
Start PDU: in frame 1
Stop PDU: in frame 6 (2.103063 : 2.103063)
dns_pdu Attributes
dns_resp: 1
dns_id: 36012
addr: 10.194.4.11
addr: 10.194.24.35Other than the pdu's tree, this one contains information regarding the relationship between the Pdus that belong to the Gop. That way we have:
-
mate.dns_req which contains the id of this dns_req Gop. This will be present in frames that belong to
dns_reqGops. -
mate.dns_req.dns_id and mate.dns_req.addr which represent the values of the attributes copied into the Gop.
-
the timers of the Gop
-
mate.dns_req.StartTime time (in seconds) passed since beginning of capture until Gop's start.
-
mate.dns_req.Time time passed between the start Pdu and the stop Pdu assigned to this Gop (only created if a
Stopcriterion has been declared for the Gop and a matching Pdu has arrived). -
mate.dns_req.Duration time passed between the start Pdu and the last Pdu assigned to this Gop.
-
-
mate.dns_req.NumOfPdus the number of Pdus that belong to this Gop
- a filterable list of frame numbers of the pdus of this Gop
Gop's timers
Note that there are two "timers" for a Gop:
-
Time, which is defined only for Gops that have been Stopped, and gives the time passed between the
Startand theStopPdus. -
Duration, which is defined for every Gop regardles of its state, and give the time passed between its
StartPdu and the last Pdu that was assigned to that Gop.
So:
-
we can filter for Pdus that belong to Gops that have been Stopped with mate.xxx.Time
-
we can filter for Pdus that belong to unstopped Gops with mate.xxx && mate.xxx.Time
-
we can filter for Pdus that belong to stopped Gops using mate.xxx.Duration
-
we can filter for Pdus that belong to Gops that have taken more (or less) time that 0.5s to complete with mate.xxx.Time > 0.5 (you can try these also as color filters to find out when response times start to grow)
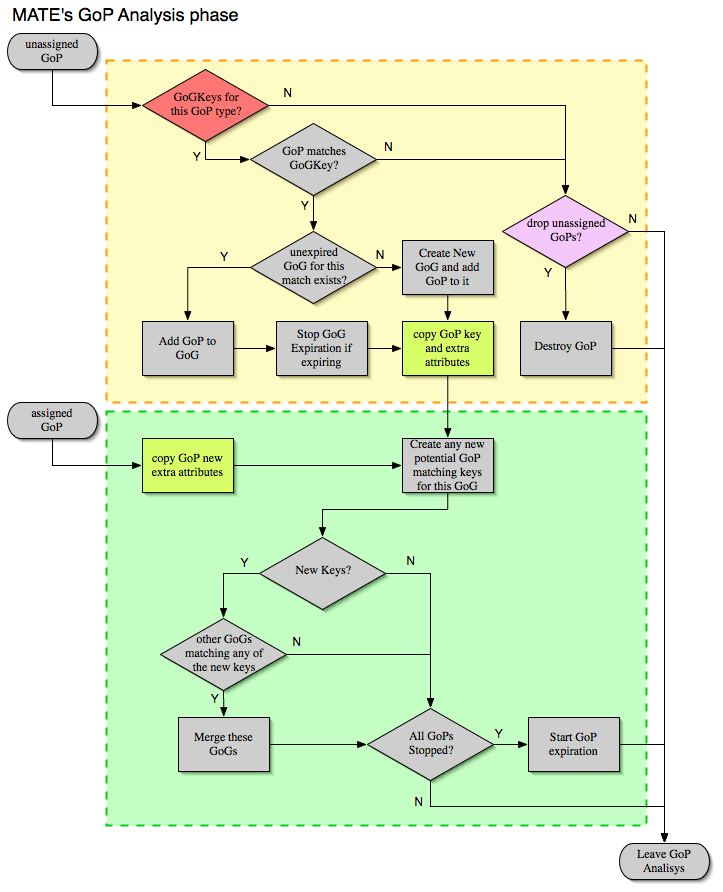
Grouping Gops together (Gog)
When Gops are created, or whenever their AVPL changes, Gops are (re)analyzed to check if they match an existent group of groups (Gog) or can create a new one. The Gop analysis is divided into two phases. In the first phase, the still unassigned Gop is checked to verify whether it belongs to an already existing Gog or may create a new one. The second phase eventually checks the Gog and registers its keys in the Gogs index.
There are several reasons for the author to believe that this feature needs to be reimplemented, so probably there will be deep changes in the way this is done in the near future. This section of the documentation reflects the version of mate as of wireshark 0.10.9; in future releases this will change.
Declaring a Group Of Groups
The first thing we have to do configuring a Gog is to tell MATE that it exists.
Gog web_use {
...
};Telling MATE what could be a Gog member
Then we have to tell MATE what to look for a match in the candidate Gops
Gog web_use {
Member http_ses (host);
Member dns_req (host);
};Getting interesting data into the Gop
Most often, also other attributes than those used for matching would be interesting. In order to copy from Gop to Gog other interesting attributes, we might use Extra like we do for Gops.
Gog web_use {
...
Extra (cookie);
};Gog's tree
mate http_pdu:4->http_req:2->http_use:1
http_pdu: 4
http_pdu time: 1.309847
http_pdu time since begining of Gop: 0.218930
http_req: 2
... (the gop's tree for http_req: 2) ..
http_use: 1
http_use Attributes
host: www.example.com
http_use Times
http_use start time: 0.000000
http_use duration: 1.309847
number of GOPs: 3
dns_req: 1
... (the gop's tree for dns_req: 1) ..
http_req: 1
... (the gop's tree for http_req: 1) ..
http_req of current frame: 2We can filter on:
-
mate.http_use.Duration time elapsed between the first frame of a Gog and the last one assigned to it.
-
the attributess passed to the Gog
- mate.http_use.host
AVPL Transforms
A Transform is a sequence of Match rules optionally completed with modification of the match result by an additional AVPL. Such modification may be an Insert (merge) or a Replace. Transforms can be used as helpers to manipulate an item's AVPL before it is processed further. They come to be very helpful in several cases.
Syntax
AVPL Transformations are declared in the following way:
Transform name {
Match [Strict|Every|Loose] match_avpl [Insert|Replace] modify_avpl ;
...
};The name is the handle to the AVPL transformation. It is used to refer to the transform when invoking it later.
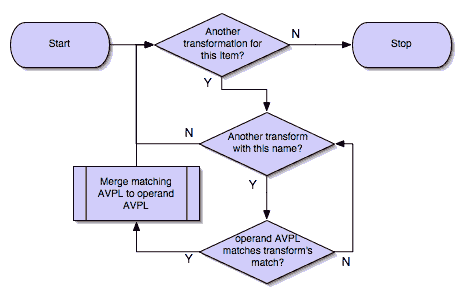
The Match declarations instruct MATE what and how to match against the data AVPL and how to modify the data AVPL if the match succeeds. They will be executed in the order they appear in the config file whenever they are invoked.
The optional match mode qualifier (Strict, Every, or Loose) is used to choose the match mode as explained above; Strict is a default value which may be omitted.
The optional modification mode qualifier instructs MATE how the modify AVPL should be used:
-
the default value
Insert(which may be omitted) causes themodify_avplto be merged to the existing data AVPL, -
the
Replacecauses all the matching AVPs from the data AVPL to be replaced by themodify_avpl.
The modify_avpl may be an empty one; this comes useful in some cases for both Insert and Replace modification modes.
Examples:
Transform insert_name_and {
Match Strict (host=10.10.10.10, port=2345) Insert (name=JohnDoe);
};adds name=JohnDoe to the data AVPL if it contains host=10.10.10.10 and port=2345
Transform insert_name_or {
Match Loose (host=10.10.10.10, port=2345) Insert (name=JohnDoe);
};adds name=JohnDoe to the data AVPL if it contains host=10.10.10.10 or port=2345
Transform replace_ip_address {
Match (host=10.10.10.10) Replace (host=192.168.10.10);
};replaces the original host=10.10.10.10 by host=192.168.10.10
Transform add_ip_address {
Match (host=10.10.10.10) (host=192.168.10.10);
};adds (inserts) host=192.168.10.10 to the AVPL, keeping the original host=10.10.10.10 in it too
Transform replace_may_be_surprising {
Match Loose (a=aaaa, b=bbbb) Replace (c=cccc, d=dddd);
};gives the following results:
- (a=aaaa, b=eeee) gets transformed to (b=eeee, c=cccc, d=dddd) because a=aaaa did match so it got replaced while b=eeee did not match so it has been left intact,
- (a=aaaa, b=bbbb) gets transformed to (c=cccc, d=dddd) because both a=aaaa and b=bbbb did match.
Usage
Once declared, Transforms can be added to the declarations of PDUs, Gops or Gogs. This is done by adding the Transform name_list statement to the declaration:
Pdu my_proto_pdu Proto my_proto Transport ip {
Extract addr From ip.addr;
...
Transform my_pdu_transform[, other_pdu_transform[, yet_another_pdu_transform]];
};- In case of PDU, the list of transforms is applied against the PDU's AVPL after its creation.
- In case of Gop and Gog, the list of transforms is applied against their respective AVPLs when they are created and every time they change.
Operation
-
A list of previously declared Transforms may be given to every Item (Pdu, Gop, or Gog), using the Transform statement.
-
Every time the AVPL of an item changes, it will be operated against all the Transforms on the list given to that item. The Transforms on the list are applied left to right.
-
Inside each of the Transforms, the item's AVPL will be operated against the Transform's Match clauses starting from the topmost one, until all have been tried or until one of them succeeds.
MATE's Transforms can be used for many different things, like:
Multiple Start/Stop conditions for a Gop
Using Transforms we can add more than one start or stop condition to a Gop.
Transform start_cond {
Match (attr1=aaa,attr2=bbb) (msg_type=start);
Match (attr3=www,attr2=bbb) (msg_type=start);
Match (attr5^a) (msg_type=stop);
Match (attr6$z) (msg_type=stop);
};
Pdu pdu ... {
...
Transform start_cond;
}
Gop gop ... {
Start (msg_type=start);
Stop (msg_type=stop);
...
}Marking Gops and Gogs to filter them easily
Transform marks {
Match (addr=10.10.10.10, user=john) (john_at_host);
Match (addr=10.10.10.10, user=tom) (tom_at_host);
}
...
Gop my_gop ... {
...
Transform marks;
}After that we can use a display filter mate.gop.john_at_host or mate.gop.tom_at_host
Adding direction knowledge to MATE
Transform direction_as_text {
Match (src=192.168.0.2, dst=192.168.0.3) Replace (direction=from_2_to_3);
Match (src=192.168.0.3, dst=192.168.0.2) Replace (direction=from_3_to_2);
};
Pdu my_pdu Proto my_proto Transport tcp/ip {
Extract src From ip.src;
Extract dst From ip.dst;
Extract addr From ip.addr;
Extract port From tcp.port;
Extract start From tcp.flags.syn;
Extract stop From tcp.flags.fin;
Extract stop From tcp.flags.rst;
Transform direction_as_text;
}
Gop my_gop On my_pdu Match (addr,addr,port,port) {
...
Extra (direction);
}NAT
NAT can create problems when tracing, but we can easily worked around it by Transforming the NATed IP address and the Ethernet address of the router into the non-NAT address:
Transform denat {
Match (addr=192.168.0.5, ether=01:02:03:04:05:06) Replace (addr=123.45.67.89);
Match (addr=192.168.0.6, ether=01:02:03:04:05:06) Replace (addr=123.45.67.90);
Match (addr=192.168.0.7, ether=01:02:03:04:05:06) Replace (addr=123.45.67.91);
}
Pdu my_pdu Proto my_proto transport tcp/ip/eth {
Extract ether From eth.addr;
Extract addr From ip.addr;
Extract port From tcp.port;
Transform denat;
}About MATE
MATE was originally written by Luis Ontanon, a Telecomunications systems troubleshooter, as a way to save time filtering out the packets of a single call from huge capture files using just the calling number. Later he used the time he had saved to make it flexible enough to work with protocols other than the ones he was directly involved with.
Imported from https://wiki.wireshark.org/Mate/Manual on 2020-08-11 23:16:34 UTC