ADwin configuration protocol (adwin_config)
The ADwin configuration protocol is used to discover, configure and update ADwin devices with Ethernet connections.
Since the ADwin devices are completely headless, all configuration options must be set remotely. To determine the IP address of a system, a UDP-broadcast based scan can be used.
History
The first ADwin real-time devices were ISA-cards that were directly built into a standard PC. Around the year 2000, the first systems with Ethernet connections were built (based on NetARM Hardware), and around 2004 new Ethernet hardware was introduced (based on Intel IXP Hardware).
Protocol dependencies
- TCP,UDP: Typically, the ADwin configuration protocol uses both TCP and UDP as its transport protocol. The port for most (but not all) ADwin configuration traffic is 7000.
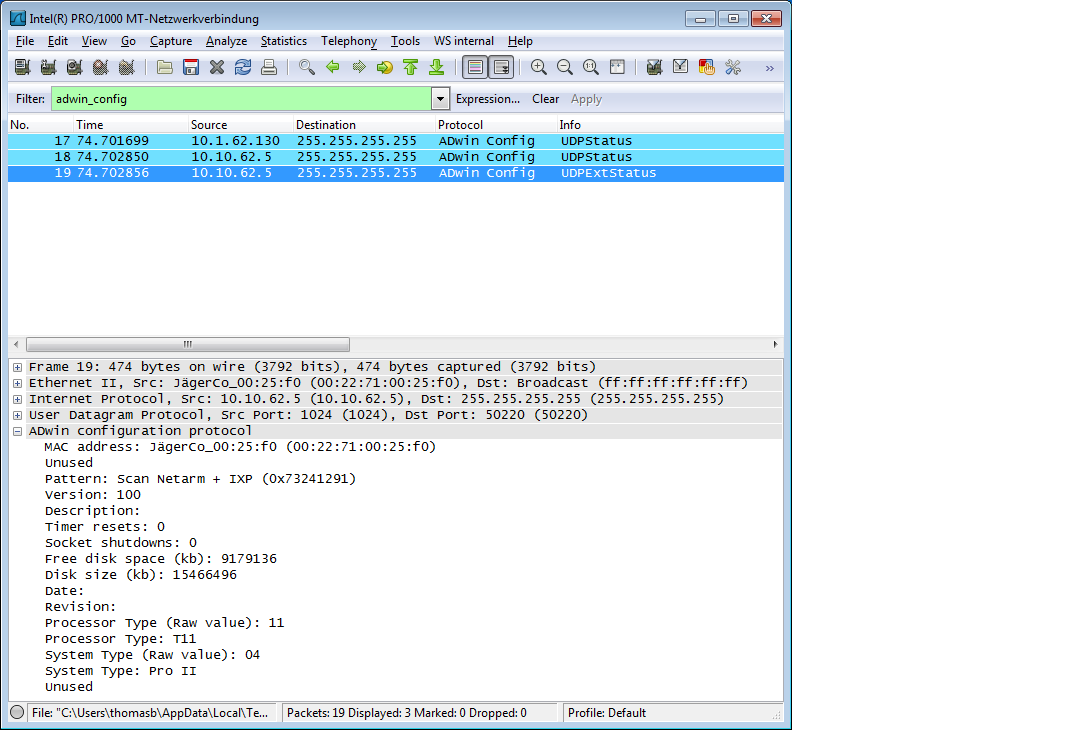
Example traffic
Wireshark
The adwin_config dissector is mostly functional, with the following exception: UDP packets for ADwin configuration are only handled by the dissector if at least one MAC address is a broadcast or in one of the following ranges:
00:50:c2:0a:20:00-00:50:c2:0a:2f:ff and 00:22:71:00:00:00-00:22:71:ff:ff:ff
Preference Settings
The dissector for the ADwin configuration protocol currently has no preferences.
Example capture file
The example capture contains a scan conversation between a PC and one ADwin system. The PC broadcasts the scan packet, and all ADwin systems in the network (only one in this example) reply with the current configuration settings.
Display Filter
A complete list of ADwin configuration display filter fields can be found in the display filter reference
Show only the adwin_config based traffic:
adwin_config Capture Filter
You cannot directly filter ADwin configuration protocols while capturing, because a few special packets do not use port 7000.
Capture most of the ADwin configuration traffic over the default port (7000):
port 7000 Imported from https://wiki.wireshark.org/Protocols/adwin_config on 2020-08-11 23:18:32 UTC