VoIP Calls
Lea esta ayuda en español en http://wiki.wireshark.org/VoIP_calls_spanish
To access the VoIP calls analysis use the menu entry "Telephony->VoIP Calls...". The current VoIP supported protocols are:
with the corresponding RTP streams.
See VOIPProtocolFamily for an overview of the used VoIP protocols.
To try out this dialog, a small capture file containing a VoIP call can be found at SampleCaptures/rtp_example.raw.gz which contains an example H323 call including H225, H245, RTP and RTCP packets.
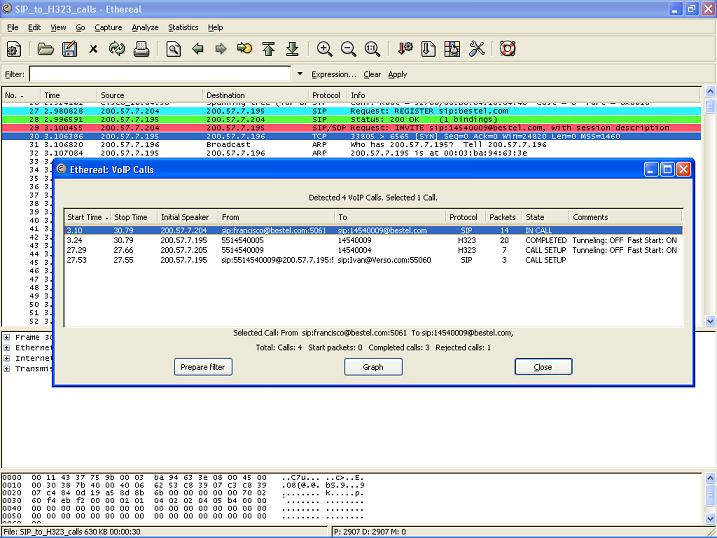
List VoIP calls
The VoIP calls list shows the following information per call:
-
Start Time: Start time of the call.
-
Stop Time: Stop time of the call.
-
Initial Speaker: The IP source of the packet that initiated the call.
-
From: For H323 and ISUP calls, this is the calling number. For SIP calls, it is the "From" field of the INVITE. For MGCP calls, the EndpointID or calling number. For UNISTIM the Terminal ID.
-
To: For H323 and ISUP calls, this is the called number. For SIP calls, it is the "To" field of the INVITE. For MGCP calls, the EndpointID or dialed number. For UNISTIM the dialed number.
-
Protocol: Any of the protocols listed above
-
Packets: Number of packets involved in the call.
-
State: The current call state. The possible values are
-
CALL SETUP: call in setup state (Setup, Proceeding, Progress or Alerting)
-
RINGING: call ringing (only supported for MGCP calls)
-
IN CALL: call is still connected
-
CANCELLED: call was released before connect from the originated caller
-
COMPLETED: call was connected and then released
-
REJECTED: call was released before connect by the destination side
-
UNKNOWN: call in unknown state
-
-
Comment: An additional comment, this is protocol dependent. For H323 calls it shows if the call uses Fast Start or/and H245 Tunneling.
Filtering a call
To prepare a filter for a particular call, just select the desired call and press "Prepare Filter" button. This will create a filter in the Main Wireshark windows to filter the packets related to this call. This is specially useful when you want to connect ISUP calls according to some CIC value.
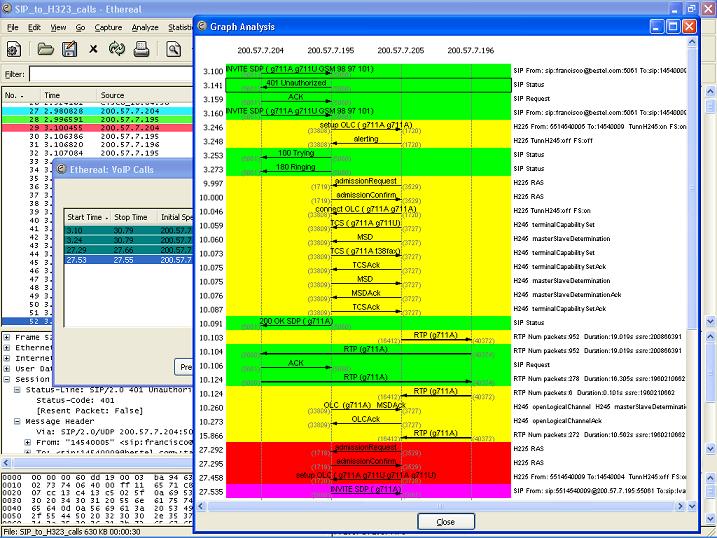
VoIP calls Graph analysis
To Graph analysis one or multiple calls from the VoIP List, select them from the list and then press the "Graph" button.
The Graph will show the following information:
-
Up to Ten columns representing an IP address each one.
-
All packets that belong to the same call are colorized with the same color
-
An arrow showing the direction of each packet in the calls
-
The label on top of the arrow shows message type. When available, it also shows the media codec.
-
The RTP traffic is summarized in a wider arrow with the corresponded Codec.
-
The comment column has protocol dependent information:
-
H323:
-
SIP:
- Shows if the packet is a "Request" or a "Staus" message.
- The INVITE message also shows the "From" and "To" fields
-
ISUP:
- The format is as follows: NetworkID-Originating Point Code -> NetworkID-Destination Point Code, CIC
-
MGCP:
- The MGCP Endpoint ID, and if the packet is a "Request" or "Response" message.
-
- Details of the message, and the sequence #.
-
RTP:
- Number of RTP packets in the stream, the duration in seconds and the SSRC field.
-
When clicking a packet in the Graph, the selected frame will be selected in the Main Wireshark window.
Playing VoIP calls
Wireshark allows you to play any codec supported by an installed plugin. Wireshark allows you to save decoded audio in .au file format. Prior to version 3.2.0, it only supported saving audio using the G.711 codec; from 3.2.0 it supports saving audio using any codec with 8000 Hz sampling.
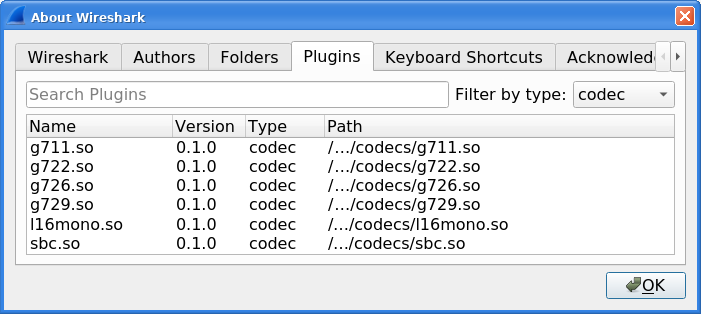
The codecs supported by Wireshark depend on the version of Wireshark you're using. The official builds contain all of the plugins maintained by the Wireshark developers, but custom/distribution builds might not include some of those codecs. To check your Wireshark follow this procedure:
-
open Help -> About Wireshark window
-
switch to Plugins tab
-
select codec as Filter by type
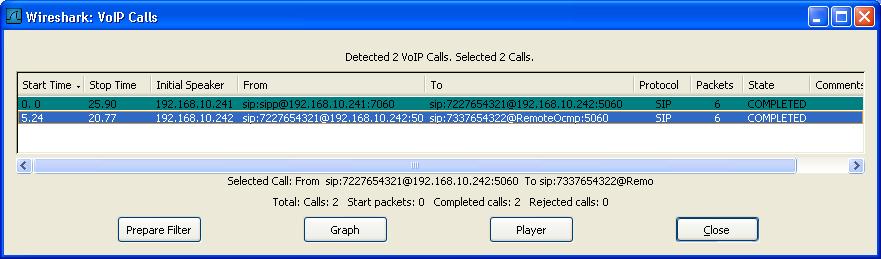
To play the RTP audio stream of one or multiple calls from the VoIP List, select them from the list and then press the "Player" button:
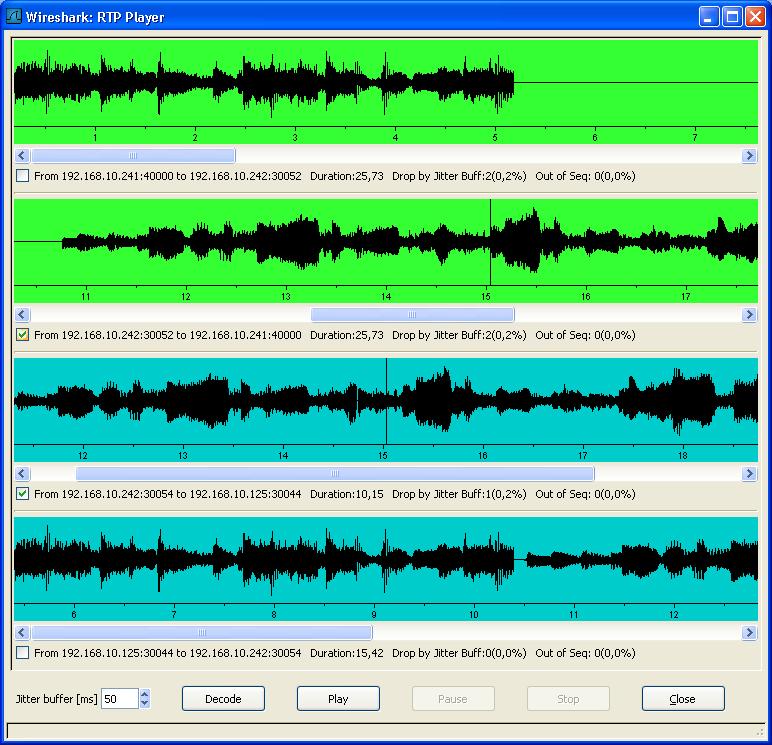
Choose an initial value for the jitter buffer and then press the "Decode button". The jitter buffer emulated by Wireshark is a fixed size jitter buffer and can efficiently be used to reproduce what clients can effectively hear during the VoIP call.
You can now see all RTP streams available for the calls that you selected:
Note that all RTP packets that are dropped because of the jitter buffer are reported ("Drop by Jitter Buff"), as well as the packets that are out of sequence (Out of Seq).
Pressing the "Play" button plays the RTP stream from within Wireshark. A progress bar indicates the position in the stream and is synchronized amongst all RTP streams that are played.
Discussion
The file rtp_example.raw.gz didn't worked for me, you may try to play this capture file VoIP call instead: SampleCaptures/SIP_CALL_RTP_G711
I have some videos on how to analyze VoIP calls using Wireshark.
Imported from https://wiki.wireshark.org/VoIP_calls on 2020-08-11 23:27:13 UTC